
Deekshabhoomi
Complete set of 2 nos of commemorative postage stamp on Deeksha Bhoomi Stupa, a sacred monument of Navayana Buddhism in Nagpur, where Babasaheb Ambedkar converted to Buddhism :



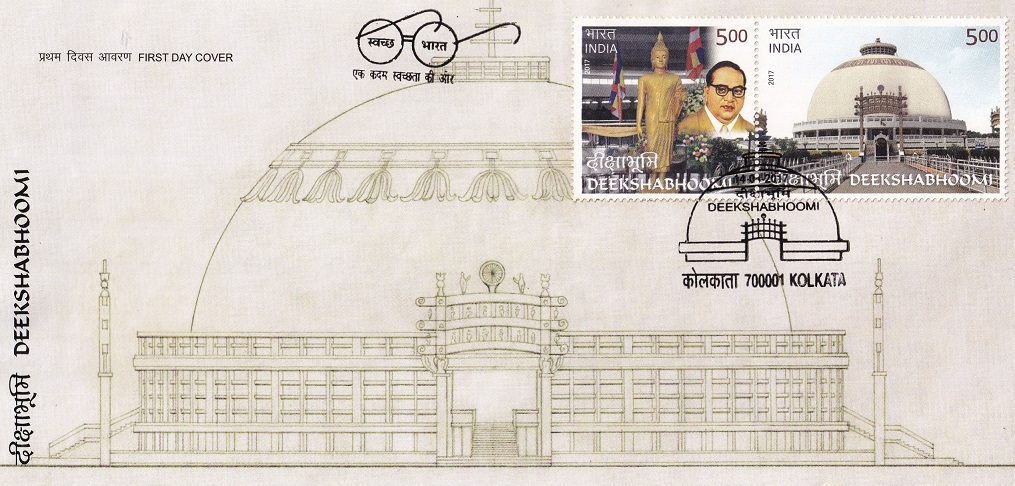
 Issued by India
Issued by India
Issued on Apr 14, 2017
Issued for : Department of Posts is pleased to release a set of two Commemorative Postage Stamps on Deekshabhoomi.
Credits :
Stamp/FDC/Brochure/Cancellation Cachet : Smt. Nenu Gupta
Type : Se–tenant set of 2 Stamps, Mint Condition
Colour : Multi Colour
Denomination : 500 Paise each
Stamps Printed : 3.10 lakh each
Printing Process : Wet Offset
Printer : Security Printing Press, Hyderabad
About :
- Deekshabhoomi is regarded as one of the most revered monuments of Buddhism. It is at this place, the architect of the Indian Constitution, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar, embraced Buddhism with nearly 4 lakhs of his followers on 14 October 1956.
- Deekshabhoomi is spread across 22 acres of land in the heart of Nagpur. Deekshabhoomi Stupa is the largest hollow stupa among all Buddhist stupas in India. The diameter is 36 meters and has a height of 22 meters. Height from ground level is 30 meters. Based on the theme of Ashok Chakra, the stupa rests on 24 pillars resembling 24 spokes. The stupa dome is constructed with concrete blocks and stands on a self-supporting concrete umbrella as a capstone. The dome is surrounded by a four meter wide veranda. Beneath the dome there is a 64 x 64 meter Prayer hall (Vihara). At the centre of stupa, Relics of Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar and an idol of Buddha is placed.
- The stupa has four doors opening in four directions. The doors lead to the large gates, which are replicas of Sanchi gate with Ashok Chakras, and statues of horses, elephants, and lions. Around the stupa, there is a garden and statues of Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar and Gautam Buddha on the south-east side of the stupa. On the east side of the stupa are built, a monastery (Bhikkhu Niwas) and two pillars depicting 22 vows and preamble of Indian constitution. The historical Bodhi Tree (Bodhi vriksha) is also planted alongside.
- The ‘Bodhi Vriksha’ at Deekshabhoomi of Bodh Gaya is a sacred fig (Pipal) tree. This Bodhi Tree is a sapling of the same Bodhi tree under which Gautam Buddha attained enlightenment. This sapling of the Bodhi Tree was brought from Anuradhapuram in Sri Lanka. The Bodhi tree at Anuradhapuram is said to be planted from the sapling of original Bodhi Tree by Sanghmitra, the daughter of Emperor Ashoka.
- Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar selected Nagpur for his conversion ceremony, as he explained in his speech that Nagpur was homeland of “Nag” people who embraced Buddhism, supported it with great efforts in its early period and propagated it throughout India.
- The emperor Ashoka the Great embraced Buddhism on the Ashwin Shukla Vijaya Dashmi, then known as Ashok Vijaya Dashmi. Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar also chose this day for embracing Buddhism. The year 1956 also coincided with 2,550th Birth Anniversary of Bhagavan Gautam Buddha.
- On Ashoka Vijaya Dashmi, 14 October 1956, Ambedkar and his wife took the oath of three Jewels “Trisaran” and five Precepts ‘Panchsheel’ from the Burmese monk Mahasthavir Chandramani from Kushinagar. Ambedkar then gave the oath of three Jewels, five precepts, and 22 Vows ‘Pratigya’ to his thousands of followers. It was after this day, Nagpur became the birthplace of Neo Buddhist movement.
- Deekshabhoomi has gained the status of a pilgrimage center of Buddhism in India. On the Ashoka Vijaya Dashmi day, called as Dhamma Chakra Pravartan Din, millions of pilgrims visit Deekshabhoomi.
- The Government of Maharashtra has declared Deekshabhoomi a status of ‘Grade-A’ pilgrimage center. Millions of people, architects and researchers visit Deekshabhoomi every year.
- Deekshabhoomi stupa was inaugurated by the then President of India Honorable Shri K. R. Narayanan on 18th December 2001.
- Text : Based on the material received from proponent.
Subscribe
Login
0 Comments
Oldest







